Hongzheng Chen Blog
AVX指令集
Mar 3rd, 2019 0这里简要介绍AVX指令集的一些基本指令,可以通过调用C++的库函数实现SIMD。
历史
见并行编程
- MME, 1996
- SSE, 1999
- AVX, 2008
- AVX2, 2011
数据类型
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
__m128 |
128-bit vector containing 4 floats |
__m128d |
128-bit vector containing 2 doubles |
__m128i |
128-bit vector containing integers |
__m256 |
256-bit vector containing 8 floats |
__m256d |
256-bit vector containing 4 doubles |
__m256i |
256-bit vector containing integers |
- integers can be chars, shorts, ints, or longs
函数命名规范(naming conventions)
_mm<bit_width>_<name>_<data_type>
<bit_width>: the return size, 128 - empty, 256 - 256<name>: describes the operation performed by the intrinsic<data_type>: the function’s primary arguments
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| ps | packed single-precision |
| pd | packed double-precision |
| epi8/epi16/epi32/epi64 | signed integers |
| epu8/epu16/epu32/epu64 | unsigned integers |
| si128/si256 | unspecified vector |
| m128/m128i/m128d m256/m256i/m256d |
input vector types |
举例:_mm256_srlv_epi64 64-bit signed int -> 256-bit vector
完整例子
#include <immintrin.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
/* Initialize the two argument vectors */
__m256 evens = _mm256_set_ps(2.0, 4.0, 6.0, 8.0, 10.0, 12.0, 14.0, 16.0);
__m256 odds = _mm256_set_ps(1.0, 3.0, 5.0, 7.0, 9.0, 11.0, 13.0, 15.0);
/* Compute the difference between the two vectors */
__m256 result = _mm256_sub_ps(evens, odds);
/* Display the elements of the result vector */
float* f = (float*) &result; // type conversion
printf("%f %f %f %f %f %f %f %f\n",
f[0], f[1], f[2], f[3], f[4], f[5], f[6], f[7]);
return 0;
}
编译时加-mavx或-mavx2
常见指令
初始化
_mm256_setzero_ps_mm256_set1_ps_mm256_set_ps: predefined values_mm256_setr_ps: reversed order
访存
_mm256_load_ps_mm256_maskload_ps(address, integer vector): mask 1 read, 0 setzeroaligned_alloc(32, 64 * sizeof(float)): 32-byte boundary
算术逻辑
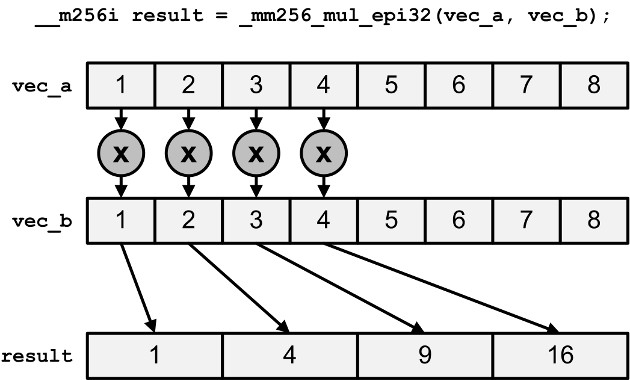
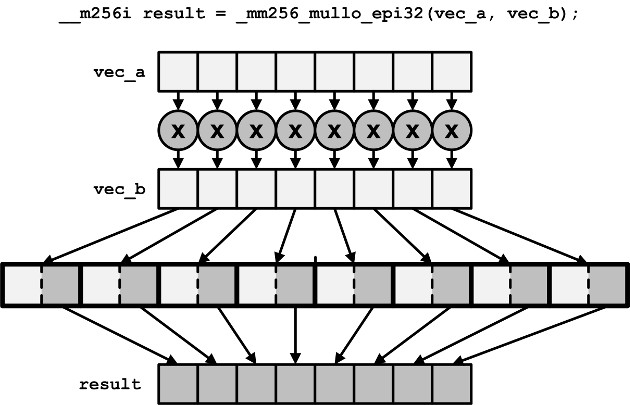
_mm256_add/sub/mul_ps_mm256_and/cmpeq_ps_mm256_hadd/hsub_ps_mm256_mullo_epi32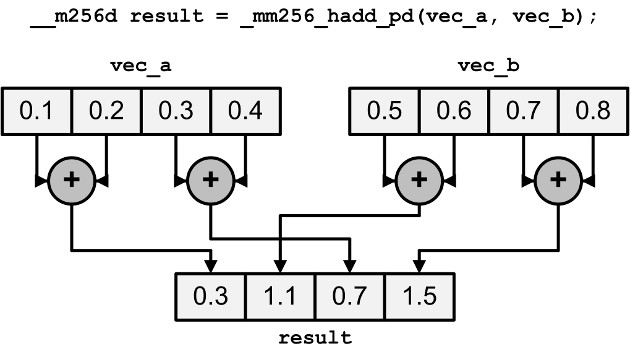
融合乘积(Fuse Multiply and Add (FMA))
编译指令-mfma
_mm_fmadd_ps:res = a * b + c_mm_fmadd_ss:res[0] = a[0] * b[0] + c[0]
重排
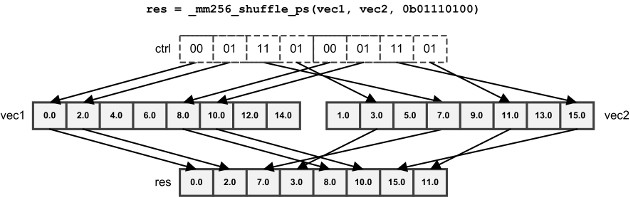
_mm256_permute_ps: based on 8-bit control value_mm256_shuffle_ps: first 2, second 2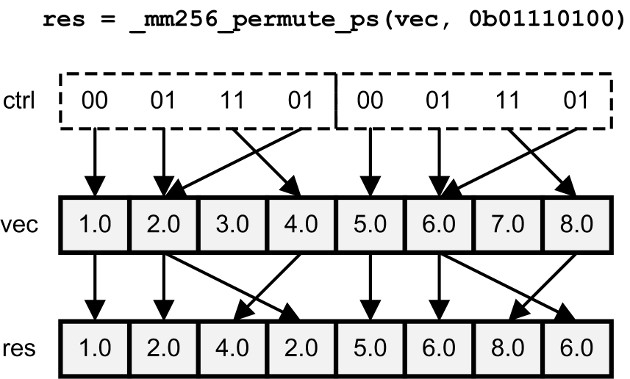
参考资料
- Crunching Numbers with AVX and AVX2, https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/874396/Crunching-Numbers-with-AVX-and-AVX