Hongzheng Chen Blog
并行编程-MPI
0消息传递模型在上个世纪90年代十分盛行,通常主进程(master process)通过对从进程(slave process)发送一个描述工作的消息来把这个工作分配给它。由于当时很多软件库都采用了这个模型,但由于不同软件定义上的区别存在大量差异,故在SC’92上制定了消息传递接口(Message Passing Interface, MPI)的标准。过了两年一个完整的接口定义(MPI-1)就已经被实现出来,这是MPI的前身。
Principles:MPI的编程模型是SPMD(单程序多数据流),异步或松同步(loosely synchronous)的方式(只有信息传递时才同步)。
基本概念
- 通信子(communicator):通信子定义了一组能够互相发消息的进程。在这组进程中,每个进程会被分配一个序号,称作秩(rank),进程间显性地通过指定秩来进行通信。通信的基础建立在不同进程间发送和接收操作。一个进程可以通过指定另一个进程的秩以及一个独一无二的消息标签(tag)来发送消息给另一个进程。
- 点对点(point-to-point)通信:一个发送者、一个接受者。
- 集体性(collective)通信:某个进程跟其他所有进程通信
常用API
MPI_Init(int* argc,char*** argv)MPI_Comm_size(MPI_Comm communicator,int* size):确定进程数目,通信子通常用MPI_COMM_WORLD取代,其中包含了当前MPI任务中所有进程MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_Comm communicator,int* rank):确定调用进程的标号,从0开始MPI_Finalize()int MPI_Test(MPI_Request *request, int *flag, MPI_Status *status):测试消息是否收到int MPI_Wait(MPI_Request *request, MPI_Status *status)
#include <mpi.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int npes, myrank;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &npes);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myrank);
printf("From process %d out of %d, Hello World!\n", myrank, npes);
MPI_Finalize();
}
编译指令
<mpi.h>mpicc、mpic++:mpicc二进制程序其实只是对gcc做了一层封装,使得编译和链接MPI程序更加方便mpirun -np 2 foo : -np 4 bar--hostfile、--host:确定主机
程序编译好后就可以被执行了。不过执行之前还需要一些额外配置,如果要在好几个节点的集群上面跑MPI,则需要配置一个host文件;单机则不需要。
需要配置的host文件会包含你想要运行的所有节点的名称。为了运行方便,需要确认所有这些节点之间能通过SSH通信,并且需要根据设置认证文件这个教程配置不需要密码的SSH访问。举例host文件如下:
$ cat host_file
cetus1:2
cetus2:2
cetus3
cetus4
$ export MPI_HOSTS=host_file
冒号后面跟的数字代表先在本机上创建这么多进程,然后再去其他机器上创建。
点对点通信
一个关键在于要重叠通信和计算
int MPI_Send(void *buf, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype, int dest, int tag, MPI_Comm comm)int MPI_Recv(void *buf, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype, int source, int tag, MPI_Comm comm, MPI_Status *status)int MPI_Isend(void *buf, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype, int dest, int tag, MPI_Comm comm, MPI_Request *request)-
int MPI_Irecv(void *buf, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype, int source, int tag, MPI_Comm comm, MPI_Request *request) - 非缓冲(non-buffered)阻塞:发送方不会返回,直到接收方执行对应的receive(实际过程是先要发握手信号),空闲(若发送接收存在时间差)和死锁会发生
- 缓冲阻塞(blocking):发送方直接将数据拷贝入指定的缓冲区后就返回,不会空闲,但有拷贝开销;接收方也会先接收到缓冲区,等到receive指令操作时才读出来;死锁依然有可能(接收方顺序不对,前面的receive被阻塞了)
- 非阻塞(non-blocking):直接返回,通常需要再次检查(check-status),用得好可以重叠通信与计算
MPI的发送模式
MPI_Send/MPI_Isend:标准模式(阻塞/非阻塞),直到使用发送缓冲才返回MPI_Bsend/MPI_Ibsend:缓冲模式,立即返回,可以使用发送缓冲- 相关操作:
MPI_buffer_attach、MPI_buffer_detach
- 相关操作:
MPI_Ssend/MPI_Issend:同步模式,不会返回直到收到posted,send+synchronousMPI_Rsend/MPI_Irsend:就绪模式,只有在matching receive已经就绪时才使用
阻塞模式常结合Wait和Test一起使用。
source可设成MPI_ANY_SOURCE,tag可设成MPI_ANY_TAG。
MPI_Send(
void* data,
int count,
MPI_Datatype datatype,
int destination,
int tag,
MPI_Comm communicator)
MPI_Recv(
void* data,
int count,
MPI_Datatype datatype,
int source,
int tag,
MPI_Comm communicator,
MPI_Status* status)
typedef struct MPI_Status {
int MPI_SOURCE;
int MPI_TAG;
int MPI_ERROR;
};
第一个参数是数据缓存。第二个和第三个参数分别描述了数据的数量和类型。MPI_send会精确地发送count指定的数量个元素,MPI_Recv会最多接受count 个元素(之后会详细讲)。第四个和第五个参数指定了发送方/接受方进程的秩以及信息的标签。第六个参数指定了使用的communicator。MPI_Recv方法特有的最后一个参数提供了接受到的信息的状态。
// 得到当前进程的 rank 以及整个 communicator 的大小
int world_rank;
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &world_rank);
int world_size;
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &world_size);
int number;
if (world_rank == 0) {
number = -1;
MPI_Send(&number, 1, MPI_INT, 1, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
} else if (world_rank == 1) {
MPI_Recv(&number, 1, MPI_INT, 0, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD,
MPI_STATUS_IGNORE);
printf("Process 1 received number %d from process 0\n",
number);
}
int MPI_Get_count(MPI_Status* status, MPI_Datatype datatype, int* count):获取精确收到的数据数目
群组通信
一对全部广播
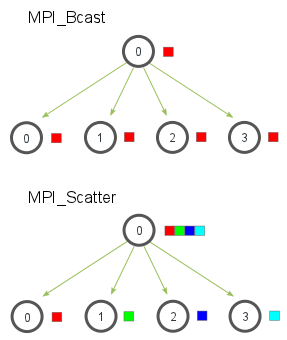
MPI_Bcast(
void* data,
int count,
MPI_Datatype datatype,
int root,
MPI_Comm communicator)
尽管根节点和接收节点做不同的事情,它们都是调用同样的这个MPI_Bcast函数来实现广播。当根节点调用MPI_Bcast函数的时候,data变量里的值会被发送到其他的节点上。当其他的节点调用MPI_Bcast的时候,data变量会被赋值成从根节点接受到的数据。
MPI_Bcast的实现使用了一个类似的树形广播算法来获得比较好的网络利用率。
MPI_Bcast给每个进程发送的是同样的数据,然而MPI_Scatter给每个进程发送的是一个数组的一部分数据,如下图所示。
MPI_Scatter(
void* send_data,
int send_count,
MPI_Datatype send_datatype,
void* recv_data,
int recv_count,
MPI_Datatype recv_datatype,
int root,
MPI_Comm communicator)
第一个参数,send_data是在根进程上的一个数据数组。第二个和第三个参数,send_count和send_datatype分别描述了发送给每个进程的数据数量和数据类型。如果send_count是1,send_datatype是MPI_INT的话,进程0会得到数据里的第一个整数,以此类推。如果send_count是2的话,进程0会得到前两个整数,进程1会得到第三个和第四个整数,以此类推。在实践中,一般来说send_count会等于数组的长度除以进程的数量。
函数定义里面接收数据的参数跟发送的参数几乎相同。recv_data参数是一个缓存,它里面存了recv_count个recv_datatype数据类型的元素。最后两个参数,root和communicator分别指定开始分发数组的了根进程以及对应的communicator。
MPI_Scatterv可解决处理器数目与分配数目不整除的问题。
int MPI_Scatterv(
void *sendbuf,
int *sendcounts, // 整数数组(长度为组的大小),其值为发送到每个进程的数据个数(整型)
int *displs, // 整数数组(长度为组的大小),每个入口i存放着相对于sendbuf的位移,此位移处存放着从进程i中接收的输入数据
MPI_Datatype sendtype,
void *recvbuf,
int recvcount,
MPI_Datatype recvtype,
int root,
MPI_Comm comm)
int MPI_Gatherv(
const void *sendbuf,
int sendcount,
MPI_Datatype sendtype,
void *recvbuf,
const int recvcounts[],
const int displs[],
MPI_Datatype recvtype,
int root,
MPI_Comm comm)
MPI_Gather跟MPI_Scatter是相反的。MPI_Gather从好多进程里面收集数据到一个进程上面而不是从一个进程分发数据到多个进程。
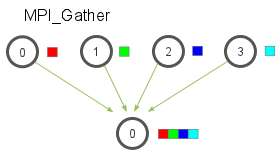
跟MPI_Scatter类似,MPI_Gather从其他进程收集元素到根进程上面。元素是根据接收到的进程的秩排序的。MPI_Gather的函数原型跟MPI_Scatter长的一样。
MPI_Gather(
void* send_data,
int send_count,
MPI_Datatype send_datatype,
void* recv_data,
int recv_count,
MPI_Datatype recv_datatype,
int root,
MPI_Comm communicator)
在MPI_Gather中,只有根进程需要一个有效的接收缓存。所有其他的调用进程可以传递NULL给recv_data。另外,别忘记recv_count参数是从每个进程接收到的数据数量,而不是所有进程的数据总量之和。
多对多通信的话,则采用MPI_Allgather,它会收集数据到所有进程上。
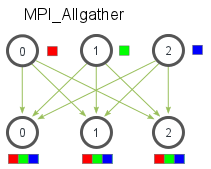
MPI_Allgather(
void* send_data,
int send_count,
MPI_Datatype send_datatype,
void* recv_data,
int recv_count,
// v: int* recvcnt, int* disp
MPI_Datatype recv_datatype,
MPI_Comm communicator)
- 阻塞到所有进程完成调用:
int MPI_Barrier(MPI_Comm comm) - 全部对一约简:
int MPI_Reduce(void *sendbuf, void *recvbuf, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype, MPI_Op op, int target, MPI_Comm comm) - 全部对一约简同时发布到全部进程:
int MPI_Allreduce(void *sendbuf, void* recvbuf, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype, MPI_Op op, MPI_Comm comm) - 全部对全部:
int MPI_Alltoall(void *sendbuf, int sendcount, MPI_Datatype senddatatype, void *recvbuf, int recvcount, MPI_Datatype recvdatatype, MPI_Comm comm) - 前缀和:
int MPI_Scan(void* sendbuf, void* recvbuf, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype, MPI_Op op, MPI_Comm comm) - 划分群组:
int MPI_Comm_split(MPI_Comm comm, int color, int key, MPI_Comm *newcomm)
自己创建通信子
int MPI_Dims_create(int nodes, int dims, int* size):nodes为期待grid里面的进程数目,通过size返回每个dim的进程数目,size也可以预设某个维度的值int MPI_Cart_create(MPI_Comm old_comm, int dims, int* size, int* periodic, int reorder, MPI_Comm *cart_comm):创建笛卡尔拓扑结构的通信子
死锁
- 顺序调整:P0 send完receive,P1 receive完后send
- 同时发送和接收:
int MPI_sendrecv(void *sendbuf, int sendcount, MPI_Datatype senddatatype, int dest, int sendtag, void* recvbuf, int recvcount, MPI_Datatype recvdatatype, int source, int recvtag, MPI_Comm comm, MPI_Status* status,如果要用同一个buffer,可用MPI_Sendrecv_replace,没有中间recv那几项参数 - 将自己的空间作为发送缓存:
Bsend+recv - 非阻塞操作:
lsend+lrecv+waitall
MPI+OpenMP
- 更低通信开销:只用MPI需要在mk个进程通信,而加上OpenMP只需在m个进程与k个线程通信
- 不同粒度的并行
- 重叠通信与计算:如3个进程都在等待,多线程加快最后一个进程
少核时共享内存带宽,纯MPI会快;多核时通信代价低,MPI+OpenMP会快