Hongzheng Chen Blog
TVM - 代码生成流程
Mar 26th, 2020 0本文主要介绍TVM的代码生成流程,即调用relay.build或tvm.build之后发生了什么,将深入到TVM的源代码进行剖析。(这里采用的依然是TVM v0.6)
首先区分两个build的区别:tvm.build主要针对单一算子(参照Tensor Expression一文),而relay.build是针对整个模型进行编译(参照GCN优化一文),而Relay最后也会调用到tvm::build做代码生成。
relay.build
通常的模型编译由以下两条语句完成。
# Build with Relay
with relay.build_config(opt_level=0):
graph, lib, params = relay.build(func, target, params=params)
跟踪细节
这里稍微提一下如何进行代码跟踪,一方面可以直接通过VS Code在函数上方Alt+单击跳转,另一方面如果想有更直观的印象,则可以利用pycallgraph进行可视化(需先用pip安装),代码如下,还是用GCN的代码编译模块。
from pycallgraph import PyCallGraph
from pycallgraph.output import GraphvizOutput
from pycallgraph import Config
graphviz = GraphvizOutput()
graphviz.output_file = 'relay_callgraph.png'
config = Config(max_depth=5)
with PyCallGraph(output=graphviz,config=config):
# Build with Relay
with relay.build_config(opt_level=0):
graph, lib, params = relay.build(func, target, params=params)
生成的Callgraph如下图所示。
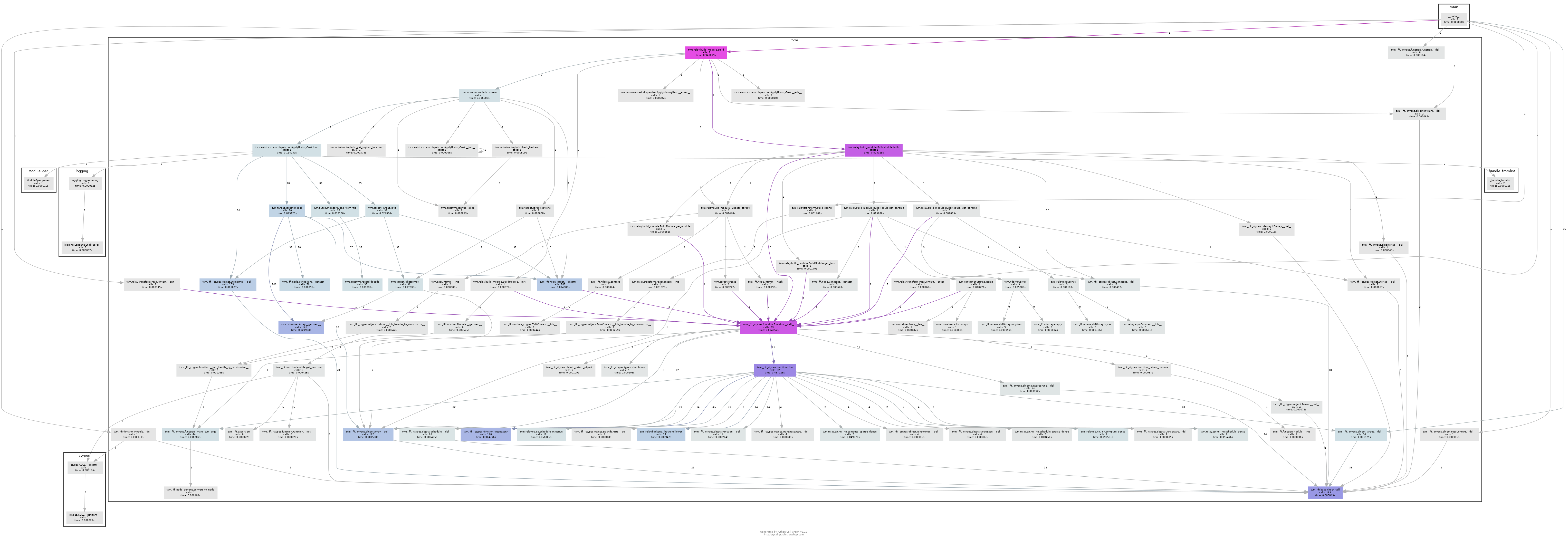
这里为放置递归过深,设置了最大深度为5,但生成的图依然很大。不过从中还是可以看出(需放大)
- 各函数之间的调用关系,如
tvm.relay.build_module.build->tvm.relay.build_module.BuildModule.build - FFI的打包调用关系,C++和Python在哪些函数上实现互调
- 深色标注的结点(执行时间长)实际上也是核心的执行步骤,即关键路径
- 结点的调用次数,如
tvm.build_module.lower调用了14次,对应的正是14个Relay算子,可见Relay IR计算图可视化。
那么对relay.build进行跟踪,跳转进来是python/tvm/relay/build_module.py(这里是因为在relay/__init__.py中将build函数直接import到relay的命名空间,因此跳过了build_module这一层),其中的build函数是build_module内的全局函数(helper)。
def build(mod, target=None, target_host=None, params=None):
# do somthing
if isinstance(autotvm.DispatchContext.current, autotvm.FallbackContext):
tophub_context = autotvm.tophub.context(list(target.values()))
else:
tophub_context = autotvm.util.EmptyContext()
with tophub_context:
bld_mod = BuildModule()
graph_json, mod, params = bld_mod.build(func, target, target_host, params)
return graph_json, mod, params
首先是寻找AutoTVM是否有预先tune好的参数记录,然后构造tophub_context,在其内部构建了BuildModule之后,才跳转到BuildModule.build,然后返回BuildModule.__init__中的内容。
class BuildModule(object):
"""Build a Relay function to run on TVM graph runtime. This class is used
to expose the `RelayBuildModule` APIs implemented in C++.
"""
def __init__(self):
self.mod = _build_module._BuildModule()
self._get_graph_json = self.mod["get_graph_json"]
self._get_module = self.mod["get_module"]
self._build = self.mod["build"]
self._optimize = self.mod["optimize"]
self._set_params_func = self.mod["set_params"]
self._get_params_func = self.mod["get_params"]
def build(self, func, target=None, target_host=None, params=None):
target = _update_target(target)
# Setup the params.
if params:
self._set_params(params)
# Build the function
self._build(func, target, target_host)
# Get artifacts
graph_json = self.get_json()
mod = self.get_module()
params = self.get_params()
return graph_json, mod, params
而_build_module._BuildModule()又通过FFI在python/tvm/relay/_build_module.py中与C++函数建立联系(tvm._ffi._cytpes.function.Function.__call__)。
from tvm._ffi.function import _init_api
_init_api("relay.build_module", __name__)
对应的C++函数在src/relay/backend/build_module.cc
runtime::Module RelayBuildCreate() {
auto exec = make_object<RelayBuildModule>();
return runtime::Module(exec);
}
TVM_REGISTER_GLOBAL("relay.build_module._BuildModule")
.set_body([](TVMArgs args, TVMRetValue* rv) {
*rv = RelayBuildCreate();
});
也就是注册了一个RelayBuildModule供调用,由于我们主要用的是build函数,因此到RelayBuildModule中找对应的函数。这里TVM又用PackedFunc做了一层封装,见下。
PackedFunc GetFunction(const std::string& name,
const ObjectPtr<Object>& sptr_to_self) final {
// ...
if (name == "build") {
return PackedFunc([sptr_to_self, this](TVMArgs args, TVMRetValue* rv) {
CHECK_EQ(args.num_args, 3);
this->Build(args[0], args[1], args[2]);
});
// ...
}
也就是调用的是this->Build,再跳转过去会指向BuildRelay。
void BuildRelay(
Function func,
const std::unordered_map<std::string, tvm::runtime::NDArray>& params) {
// Optimize input Relay Function and returns Relay Module
relay::Module relay_module = Optimize(func, targets_, params);
// Get the updated function.
func = relay_module->Lookup("main");
// Generate code for the updated function.
graph_codegen_ = std::unique_ptr<GraphCodegen>(new GraphCodegen());
graph_codegen_->Init(nullptr, targets_);
graph_codegen_->Codegen(func);
ret_.graph_json = graph_codegen_->GetJSON();
ret_.params = graph_codegen_->GetParams();
auto lowered_funcs = graph_codegen_->GetLoweredFunc();
if (lowered_funcs.size() == 0) {
LOG(WARNING) << "no lowered funcs exist in the compiled module";
} else {
ret_.mod = tvm::build(
lowered_funcs,
target_host_,
BuildConfig::Current());
}
}
经过多番跳转,终于到达build的核心模块,再来看TVM逐步做的工作。
- 优化
- 计算图生成
- 后端代码生成
优化
先是优化Optimize,可以看到这里的优化主要是设备无关的优化,是graph-level的针对tensor运算的优化。(这里的优化pass都已经在C++中实现,先前版本的NNVM似乎还是在Python中调用)
relay::Module Optimize(
Function func,
const TargetsMap& targets,
const std::unordered_map<std::string, runtime::NDArray>& params) {
// BindParamsByName(func, params)
// Perform Module->Module optimizations.
relay::Module relay_module = relay::ModuleNode::FromExpr(func);
Array<Pass> pass_seqs;
// Run all dialect legalization passes.
// ...
pass_seqs.push_back(transform::SimplifyInference());
//
// ...fskip
//
pass_seqs.push_back(transform::EliminateCommonSubexpr(fskip));
pass_seqs.push_back(transform::CombineParallelConv2D(3));
pass_seqs.push_back(transform::CombineParallelDense(3));
pass_seqs.push_back(transform::FoldConstant());
pass_seqs.push_back(transform::FoldScaleAxis());
pass_seqs.push_back(transform::CanonicalizeCast());
pass_seqs.push_back(transform::CanonicalizeOps());
// ...AlterOpLayout
pass_seqs.push_back(transform::FoldConstant());
// Create a sequential pass and perform optimizations.
transform::Pass seq = transform::Sequential(pass_seqs);
// ... judge & do
relay_module = seq(relay_module);
// Handle heterogeneous compilation.
transform::PassContext pass_ctx = PassContext::Current();
if (targets_.size() > 1) {
relay_module =
RunDeviceAnnotationPass(relay_module, pass_ctx->fallback_device);
}
// Fuse the operations if it is needed.
relay_module = transform::FuseOps()(relay_module);
relay_module = transform::InferType()(relay_module);
CHECK(relay_module.defined());
return relay_module;
}
计算图生成
对应GraphCodegen类,以同样的方式调用src/relay/backend/build_module.cc中的relay.build_module._GraphRuntimeCodegen(一样是FFI),然后跳转至src/relay/backend/graph_runtime_codegen.cc,其中已经用TVM_REGISTER_GLOBAL注册了对应函数,即用GraphRuntimeCodegenModule生成对应Object。
因此实际graph_codegen_->Codegen的函数是一个PackedFunc,定义在GraphRuntimeCodegen.Codegen,用来将relay::Function func进行遍历,然后生成计算图。
后端代码生成
Relay得到lower后的函数,最后一步则是交给tvm::build做代码生成,跳转到src/codegen/build_module.cc中的build函数(注意这里重载了几个版本),然后跳转到核心build,注意这里的build函数支持异构编译,只要再inputs划分好不同硬件设施即可。
// Build for heterogeneous execution.
runtime::Module build(const Map<Target, Array<LoweredFunc>>& inputs,
const Target& target_host,
const BuildConfig& config) {
Array<LoweredFunc> fhost_all;
std::vector<runtime::Module> device_modules;
Target target_host_val = target_host;
if (!target_host.defined()) {
for (const auto& it : inputs) {
if (it.first->device_type == kDLCPU) {
target_host_val = it.first;
break;
}
}
}
if (!target_host_val.defined()) {
target_host_val = DefaultTargetHost(target_host_val);
}
for (const auto& it : inputs) {
auto host_dev_funcs =
split_dev_host_funcs(it.second, it.first, target_host_val, config);
auto& fhost = host_dev_funcs[0];
auto& fdevice = host_dev_funcs[1];
// Get the module for a certain target.
runtime::Module mdev = DeviceBuild(fdevice, it.first);
for (const auto& it : fhost) {
fhost_all.push_back(it);
}
device_modules.push_back(mdev);
}
runtime::Module mhost = codegen::Build(fhost_all, target_host_val->str());
// Import all modules
for (const auto& it : device_modules) {
if (it.operator->()) {
mhost.Import(it);
}
}
return mhost;
}
当中最最核心的则是mhost = codegen::Build,最后跳转过去就开始调用代码生成模块了(src/codegen/codegen.cc)。
runtime::Module Build(const Array<LoweredFunc>& funcs,
const std::string& target) {
// do something
std::string build_f_name = "codegen.build_" + mode;
// the build function.
const PackedFunc* bf = runtime::Registry::Get(build_f_name);
runtime::Module m = transformed_funcs.empty() ?
(*bf)(funcs, target) :
(*bf)(transformed_funcs, target);
return m;
}
以生成LLVM IR为例,codegen.build_llvm会在src/codegen/llvm/llvm_module.cc注册,然后调用同个文件中的LLVMModuleNode->Init。这时会跳转到src/codegen/llvm/codegen_llvm.cc中的CodeGenLLVM类进行代码生成。
tvm.build
用tvm.build对算子进行编译则是按照以下方式进行调用,例子来自Tensor Expression。
s = tvm.create_schedule(C.op)
tgt = "llvm" # "cuda"
fadd = tvm.build(s,[A,B,C],target=tgt,name="myadd")
调用tvm.build后首先跳转到python/tvm/build_module.py,其中的build函数主要做两个步骤:
- lower高层次代码
- 后端代码生成
代码变换
lower高层次代码对应的是
flist = lower(inputs,args,name=name,binds=binds)
而lower函数同样在python/tvm/build_module.py中,类似于relay.build中的Optimize,但这里执行的是operator-level的优化,主要针对循环变换。
def lower(sch,
args,
name="default_function",
binds=None,
simple_mode=False):
# initialization
# Phase 0
if isinstance(sch, schedule.Schedule):
stmt = form_body(sch)
for f in lower_phase0:
stmt = f(stmt)
compact = ir_pass.VerifyCompactBuffer(stmt)
binds, arg_list = get_binds(args, compact, binds)
# Phase 1
stmt = ir_pass.RewriteForTensorCore(stmt, sch, binds)
stmt = ir_pass.StorageFlatten(stmt, binds, 64, cfg.instrument_bound_checkers)
stmt = ir_pass.CanonicalSimplify(stmt)
for f in lower_phase1:
stmt = f(stmt)
# Phase 2
if not simple_mode:
stmt = ir_pass.LoopPartition(stmt, cfg.partition_const_loop)
if cfg.disable_vectorize:
stmt = ir_pass.SkipVectorize(stmt)
else:
stmt = ir_pass.VectorizeLoop(stmt)
stmt = ir_pass.InjectVirtualThread(stmt)
stmt = ir_pass.InjectDoubleBuffer(stmt, cfg.double_buffer_split_loop)
stmt = ir_pass.StorageRewrite(stmt)
stmt = ir_pass.UnrollLoop(
stmt,
cfg.auto_unroll_max_step,
cfg.auto_unroll_max_depth,
cfg.auto_unroll_max_extent,
cfg.unroll_explicit)
for f in lower_phase2:
stmt = f(stmt)
# Phase 3
stmt = ir_pass.Simplify(stmt)
stmt = ir_pass.RemoveNoOp(stmt)
if not cfg.disable_select_rewriting:
stmt = ir_pass.RewriteUnsafeSelect(stmt)
for f in lower_phase3:
stmt = f(stmt)
# Instrument BoundCheckers
if cfg.instrument_bound_checkers:
stmt = ir_pass.InstrumentBoundCheckers(stmt)
if simple_mode:
return stmt
return ir_pass.MakeAPI(stmt, name, arg_list, 0, cfg.restricted_func)
优化Pass的主体实施都在src/api/api_pass.cc中,以tvm.ir_pass进行注册(注意由于C++函数中已经在tvm的命名空间里,故搜索时直接搜ir_pass才会出来对应的API)。
代码生成
lower完之后就进入到后端代码生成,对应build函数中的
mhost = codegen.build_module(fhost_all, str(target_host))
同样的原理,跳转至tvm/codegen.py,初始化tvm.codegen的API codegen._Build,调用FFI,跳转至src/api/api_codegen.cc,最后跳转至src/codegen/codegen.cc中的tvm::Build,之后的后端代码生成则与relay.build相同。
References
- TVM Codebase Walkthrough by Example, https://docs.tvm.ai/dev/codebase_walkthrough.html
- TVM图编译器Relay简单探究 - 郑思泽的文章 - 知乎, https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/91283238
- 谢睿峰, TVM/VTA代码生成流程, https://krantz-xrf.github.io/2019/10/24/tvm-workflow.html
- https://discuss.tvm.ai/t/relationship-between-tvm-build-and-relay-build/4166